Urine (Microscopy, Culture & Sensitivity)
Alias: N/A
Discipline: Clinical Microbiology
Test information: The isolation of organisms known to cause urinary tract infections. Where applicable to determine antimicrobial susceptibility results.
Availability: Available locally Monday - Sunday during routine hours: 08:45 - 21:00.
Available out of hours on telephone request for children > 3 months old until 23:00. Children < 3 months old available any time by telephone request from registrar or paediatric consultant.
Turnaround Time: 24 hours (Microscopy)
48 hours (Culture)
- Specimen Type(s)
-
- Urine;
- Other Acceptable Specimen Type(s)
-
- Mid-Stream Urine;
- Catheter Urine;
- Clean Catch Urine;
- Suprapubic Aspirate;
- Cystoscopy Urine;
- Ureteric Urine;
- Ileal Conduit Urine;
- Urostomy Urine;
- Nephrostomy Urine
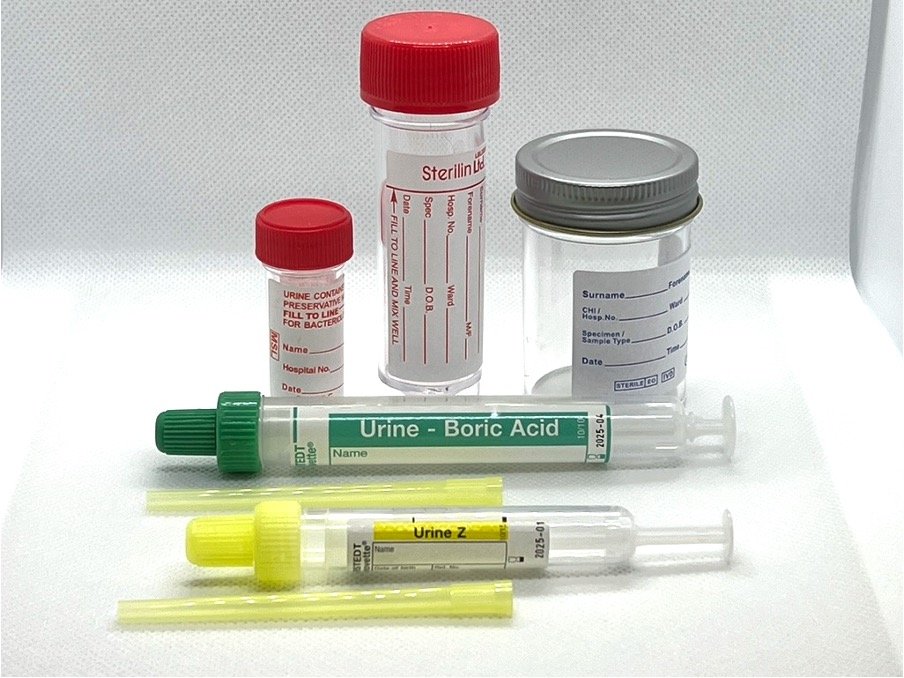
- Specimen Container - Adult
-
- Boric Acid Tube;
- Sterile CE-marked Universal Container;
- Urine Monovette Primary Tube;
- Specimen Container - Paediatric
-
- Boric Acid Tube;
- Sterile CE-marked Universal Container;
- Urine Monovette Primary Tube;
- Analytes
-
- Culture & Sensitivity;
- Part of a test profile?
- No
- Volume (min) of sample to be sent to laboratory
-
- Minimum sample volume in non-boric container: 1.2mL
- Boric Acid Containers must be filled to the appropriate line shown on the container.
- Automated microscopy cannot be performed on specimens <1mL.
- Patient Preparation, Sample Handling and Transport
-
- Non-boric samples are stable for 24 hours but should be processed within 4 hours if possible.
- Boric acid samples are stable for 48 hours; ensure the contents are mixed well.
- Specimens should be transported to the laboratory without delay during normal working hours.
- If transport is delayed store non-boric samples at 2-8 °C.
- If transport is delayed store boric samples at room temperature.
- Mid-stream urine advised where possible.
- No pad urines are accepted.
- Catheter specimens should be collected only if the patient is pyrexial or systemically unwell.
- Catheter specimens should be obtained aseptically from a sample port in the catheter tubing or by aseptic aspiration of the tubing. The specimen should not be obtained from the collection bag.
- The presence of epithelial cells on microscopy indicates contamination and the culture result should be interpreted with caution.
- If repeat specimens yield results which indicate contamination you may wish to use instrumentation which facilitates the collection of urine avoiding contamination.
- Long-term catheters are invariably colonized with one or more micro-organisms. Treatment with antibiotics should be reserved for those with signs of systemic infection.
- Maximum add on time
- N/A
- Units and Reference Ranges / Interpretation
-
- Microscopy Report
- White blood cells: x 106/L (Normal range = 0 - 40)
- Squamous epithelial cells : x 106/L (Normal range = 0 - 50)
More than 40 x 106/L white blood cells is considered to be significant pyuria.
- UKAS number
- 8869
- UKAS accredited test?
- Yes
- Comments
-
Susceptibility Testing: Each susceptibility category is defined by breakpoints specific for each species and agent. The breakpoints are minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) and describe the amount of agent required to inhibit the growth of the organism.
The definitions of (S),(I), and (R) emphasize the close relationship between the susceptibility of the organism and the exposure of the organism at the site of infection.
Susceptible (S): High likelihood of therapeutic success with standard dosing.
Susceptible Increased Exposure (I): High likelihood of therapeutic success with increased dosing.
Resistant (R): High likelihood of therapeutic failure.Useful Links:
If you have any queries about a test or results interpretation please contact us.
Last updated: 01-06-2023